“The future is already here – it’s just not evenly distributed” – William Gibson
AI is not just a futuristic technology that can radically change our lives, and potentially eliminate jobs and humans. It is something that is currently used in many industries and applications. There are numerous and proven AI techniques, libraries, SDKs, APIs and vendor platforms that can be integrated into existing Mobile & Web Applications, to increase customer adoption, revenue per user and improve UX. There are also numerous opportunities develop new products, applications and platforms.
This page helps readers get answers to the following questions
- What is Artificial Intelligence?
- What is Machine Learning?
- What is Deep Learning?
- What are the Key Steps / Processes?
- How can we use this knowledge to solve business problems?
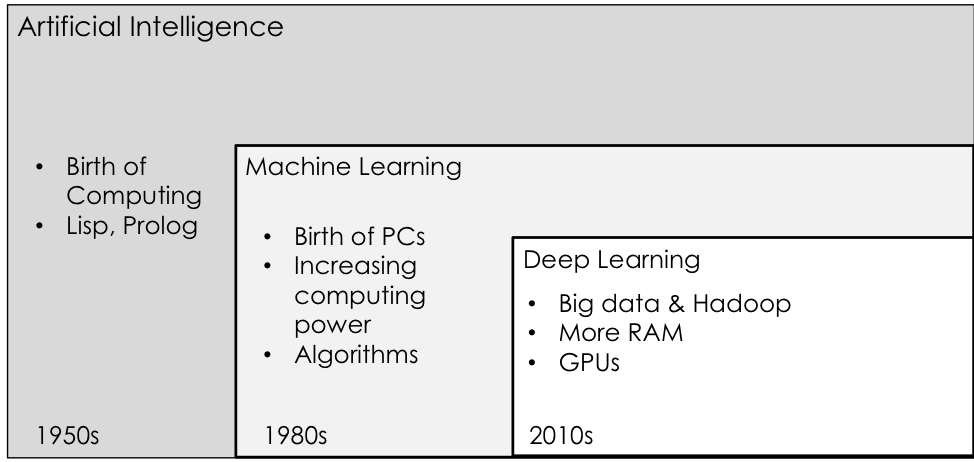
History of AI
Definition & Examples
What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is the process of building systems that can think and act intelligently. Intelligence is defined as human like or rational (not necessarily optimal). In practice, however, AI has been able to act rationally or even optimally at times exceeding human ability in one specific task (defined as Narrow AI). AI’s ability think rationally and act humanly is more limited. Furthermore, current AI does not have the ability to think humanly. Despite all of the above, AI is very useful and has a very promising future.
AI is also a very a broad topic, and includes Machine Learning. It is important to recognize that there are many intelligent systems that are engineered solutions (i.e. pre-programmed algorithms), that do not incorporate any learning (not Deep Learning nor any Machine Learning).
Some examples of AI that do not incorporate Machine Learning:
Expert systems based on rule-based reasoning and case-based reasoning have been around for a long time. Rule-based system are a series of if-then rules where rules are input by domain experts (i.e. not developers) and can be added outside development cycle (i.e. not during build time)
Classical search techniques (e.g. breadth-first search, depth first search) and more advanced search techniques (e.g. adversarial search) can be used to provide driving directions
Some of the most advanced robots depend good old electrical engineering control systems. This particular robot is likely using ZMP and its variations
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a field of AI. Here the applications learn from data using statistical techniques. Hence rules and formulas applied are not always pre-programmed (or explicitly programmed) but are learnt.
Machine Learning is split into three main types of learning
Supervised Learning: Objective here is to classify / detect (called classification – e.g. recognize handwritten digits or a face) or predict value (called regression – e.g. calculate Credit Score). The challenge with supervised learning is that the data needs to be accurately labeled (in-addition to being available).
Unsupervised Learning: Often used to detect patterns in the data without explicit labeling (algorithm may apply labeling but manual labeling is not necessary). Anomaly detection is a form of unsupervised learning used in security and infrastructure monitoring.
Historically, unsupervised learning offered limited value by itself. However, it is currently used for word embeddings (used in search, text classification, etc.), anomaly detection and elsewhere where it is adding significant value.
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning enables applications to take sequential actions in order achieve an identified objective – for example, play a game of Chess / Go. Reinforcement learning, is a general approach and is used in numerous areas such as games, control systems (e.g. robots, self-driving cars), swarm intelligence, genetic algorithms, etc.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is an ANN (Artificial Neural Network) that has more than one hidden layer. Many of the recent advances in AI (e.g. AlphaGo, Computer Vision, Speech Recognition) have come as result of Deep Learning.
Deep Learning by its very nature requires a lot computing power, and is now possible due to use of GPUs and increased RAM. However, Deep Learning requires more data for training. Hence, in scenarios where there is insufficient labelled training data, traditional Machine Learning is a more viable option.
What are the Key Steps / Processes?
Intelligent systems in general require a lot more to train and/or validate, relative to traditional applications. In general these systems go through three distinct process – 1) Data Pre-processing / Governance, 2) Feature Engineering and 3) Modelling.

Data Pre-processing / Governance: Assume you want to search and classify documents. If all the documents are either HTML, PDF or DOC format, then removing HTML, PDF and DOC specific tags would be the first task in data pre-processing. Subsequently, you may choose remove special characters (e.g. “-“, “!”) and then convert all of them to lower case.
When trying to train New York Cab Fare prediction there may be a few unusually high cab fares that should be removed from the training data. The rationale is that the extreme data points (or edge cases) may have been caused by major accident and unusually bad weather. This is also considered feature engineering.
Feature Engineering: You are trying to estimate New York Cab Fare based on pickup location, drop-off location, and date & time. Based on experience you know that cab fare is based on duration of the trip, and some of the primary factors influencing duration are distance (although driving distance is not the same distance, distance is a reasonable heuristic) and time of day (e.g. weekday, weekend, morning rush hour, evening rush hour). This is feature engineering.
Modelling: Modelling is the process of applying Machine Learning techniques such as Neural Networks (Shallow and Deep) and other Statistical Learning techniques.
Notes:
- Both data pre-processing / governance and feature engineering require domain expertise.
- AI systems that do not incorporate machine learning may not have a distinct modelling process.
- Deep Learning systems often remove Feature Engineering to remove bias.
How can we use this knowledge to solve business problems?
When considering using AI for solving business problems the solution can be placed into three buckets – 1) Thinking and acting like humans, 2) Enhancing computing capabilities and 3) Hybrid solutions.
- Thinking and acting like humans: While many of these solutions focus on reducing cost by minimizing dependency on humans, the ultimate goal is to increase service availability and improve quality. Examples,
- Enhancing computing capabilities: Solutions belonging to this category can increase revenue, and help reduce cost and risk.
- Mobile & Web Analytics
- Interactive Marketing
- Spam Filtering
- Fraud Detection
- Hybrid solutions: These solutions while providing many benefits are more likely to deliver disruptive paradigms (especially short-term).